TYPES OF HYDROGEN
Hydrogen can be sorted into various groups based on the techniques employed to produce it. These categories reflect the different levels of environmental impact and carbon emissions linked to hydrogen production methods. The trend is towards increasing the share of green and blue hydrogen to diminish the carbon footprint of the hydrogen industry and facilitate the transition to a more sustainable energy system. The classification frequently revolves around the carbon discharges linked to each method. Behold some of the most popular groups
- Grey hydrogen is the product of fossil fuels, predominantly natural gas. It is made via steam methane reforming (SMR) or coal gasification. This technique is the most widespread and cost-effective but spews out substantial quantities of carbon dioxide, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions.
- Blue hydrogen is created using the same methods as grey hydrogen but with an additional step of carbon capture and storage (CCS). The carbon dioxide released during hydrogen production is trapped and stored underground, reducing the carbon discharges related to the process.
- Green hydrogen is made using renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, or hydroelectric power, by means of electrolysis. Renewable electricity is employed to divide water into hydrogen and oxygen, without any carbon emissions. Green hydrogen is regarded as the most eco-friendly and sustainable method of hydrogen production.
- Turquoise hydrogen is produced by combining natural gas and renewable energy sources. The natural gas is partially oxidized with oxygen or steam, and the ensuing carbon emissions are captured and stored via CCS. The renewable energy component helps decrease the overall carbon footprint of the production process.
- Brown hydrogen refers to hydrogen made from coal by employing gasification processes. It is an older and less frequent method that isn’t widely used today due to its high carbon emissions and detrimental environmental impact.
- Purple hydrogen is obtained via nuclear energy as the primary power source for electrolysis. Nuclear power supplies the electricity required to divide water into hydrogen and oxygen, resulting in zero carbon emissions during the production process.
What is green Hydrogen?
Green hydrogen is generated by harnessing the power of renewable sources, like solar, wind, or hydroelectricity. This involves the electrification of water, which undergoes a split of its atomic components – oxygen and hydrogen – through an electric current. This current is powered by clean energy sources, ensuring a minute carbon footprint.
The term “green” in green hydrogen depicts its eco-friendly aspect. Unlike traditional hydrogen manufacturing processes, which depend on fossil fuels such as natural gas, green hydrogen production has no greenhouse gas emissions. It is perceived as a sustainable and clean energy carrier that can be used for various purposes, including transportation fuel, industrial processes, and energy storage.
Green hydrogen has the potential to decarbonize sectors that are arduous to electrify directly, such as long-distance transportation and heavy industry. Its adoption can contribute to the reduction of carbon dioxide emissions and facilitate the transition to a sustainable and low-carbon energy system.
What is inside the Green Hydrogen Plant?
These constituents collaborate to facilitate the production, storage, and distribution of green hydrogen, providing a sustainable and low-carbon energy carrier. A verdant hydrogen production facility, utilizing renewable energy sources, typically comprises of the following components:
- Green hydrogen production plants depend on renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, or hydroelectric power. These sources provide the electricity required for the electrolysis process.
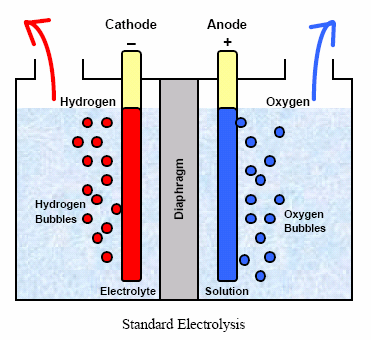
- The electrolyzer is an indispensable component that executes the electrolysis process. It comprises of an anode and a cathode separated by an electrolyte. When an electric current is applied, water (H2O) is cleaved into hydrogen (H2) at the cathode and oxygen (O2) at the anode.
- The power conversion system is liable for converting the electrical energy from the renewable energy sources into the appropriate form for the electrolyzer. It may incorporate transformers, inverters, or other power conditioning equipment.
- Water is a fundamental input for the electrolysis process, and it requires treatment and purification before entering the electrolyzer. This typically entails filtration, demineralization, and removing impurities that could impact the effectiveness and durability of the electrolysis process.
- After production, the hydrogen gas necessitates compression and storage for future use. Compressors are utilized to boost the pressure of the hydrogen gas, making it suitable for storage and transportation. Storage options may include compressed gas cylinders, subterranean caverns, or other hydrogen storage technologies.
- Depending on the specific requirements of the application, the yielded hydrogen may require further purification and conditioning. This could involve eliminating impurities such as moisture, carbon dioxide, or other trace elements to meet the desired quality standards.
TYPES OF HYDROGEN
Hydrogen can be sorted into various groups based on the techniques employed to produce it. These categories reflect the different levels of environmental impact and carbon emissions linked to hydrogen production methods. The trend is towards increasing the share of green and blue hydrogen to diminish the carbon footprint of the hydrogen industry and facilitate the transition to a more sustainable energy system. The classification frequently revolves around the carbon discharges linked to each method. Behold some of the most popular groups
Different Types of Electrolyzers
The hydrogen production process through electrolysis utilizes various types of electrolyzers. It’s noteworthy that these electrolyzers differ in operating temperatures, electrolyte materials, efficiency levels, and application suitability. The type of Electrolyzer employed is determined by several factors, including the scale of production, the desired hydrogen purity, efficiency requirements, and cost considerations.
Renewable Energy & Green Hydrogen
Renewable energy and green hydrogen are intimately linked in the realm of hydrogen production. Renewable energy sources, like solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, generate electricity sans any direct emission of greenhouse gases. To power the electrolysis process, which cleaves water into hydrogen and oxygen, green hydrogen production harnesses this clean and sustainable electricity.
The connection between renewable energy and green hydrogen empowers the production of a clean, sustainable, and versatile energy carrier, which can contribute to the transition to a low-carbon economy and help mitigate climate change.
The utilization of Om Shre Eenter Prises energy for green hydrogen fosters a sustainable energy ecosystem that promotes resilience, reduces reliance on fossil fuels, and mitigates climate change. By combining the benefits of solar power, wind power and green hydrogen, Om Shre Eenter Prises plays a vital role in helping you with your journey towards a net-zero carbon economy, offering a pathway to a sustainable and greener future.

